Market
Day-to-day management of the single day-ahead and intraday coupling
According to Art. 10 CACM, TSOs cooperate with Nominated Electricity Market Operators (NEMOs) to organise the day-to-day management of the single day-ahead and intraday coupling. ENTSO-E facilitates the discussion. Although the overall governance structure of the single intraday and day-ahead coupling has been previously agreed, the governance principles were jointly agreed by NEMOs and TSOs in the first quarter of 2019. This work helps jointly organise the further development of the market coupling by defining the responsible bodies and classifying of the decisions to be taken by each body, as well as helping to define the criteria for prioritising the functionalities to be developed.
After ACER’s decision of January 2019 on the all TSOs proposal for a single methodology for pricing intraday cross-zonal capacity in accordance with Art. 55.3, requesting amendments to the “TSOs’ common set of requirements for an efficient capacity allocation in the intraday timeframe”, TSOs developed the requirements and submitted them to the NEMOs. The requirements were included in the annex of the algorithm methodology submitted by the NEMOs in July 2019 in accordance with Art. 37.
The second wave of the European Single Intraday Coupling (SIDC) went live in November 2019, expanding the continuous trading of electricity across Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Romania and Slovenia4.
Key dates & documents
24 Jan 2019
“ACER Decision on the Methodology for pricing intraday cross-zonal capacity” (Annex I)
31 Jul 2019
Submission to ACER of the amendments to Algorithm Methodology
4 They join the existing countries already operating the SIDC: Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, The Netherlands, Portugal, Spain and Sweden.
Other CACM evolutions
In accordance with the CACM Regulation, in 2019 CCRs delivered day-ahead and intraday capacity calculation methodologies (Art. 20.25), methodologies for coordinated redispatching and countertrading (Art. 35.1) and redispatching and countertrading cost sharing methodology (Art. 74.1). After an amendment request from all NRAs, in January 2019 all TSOs submitted the final version of the methodology for calculating scheduled exchanges resulting from single intra-day coupling” in accordance with Article 56.1.
5 Article 21.1 provides with further details on the expected content of the proposal.
| DA and ID CapCalc (Art. 20.2) | RD and CT (Art. 35.1) | SchedExc single ID coupling (Art. 56.1) | RD and CT cost sharing (Art. 74.1) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All TSOs | n/a | n/a | Approved 8 Feb 2019 | n/a |
| Italy North | DA and ID submitted 16 Aug 2019 Public consultation 15 Oct – 17 Nov 2019 | Approved 18 May 2019 | n/a | Already submitted |
| Core | Approved 21 Feb 2019 | Submitted 22 Feb 2019 | n/a | |
| SWE | Already approved | Approved 15 May 2019 | n/a | Approved 15 May 2019 |
| IU | Already approved | Submission 1st amendment 17 May 2019 | n/a | Submission 1st amendment 17 May 2019 |
| SEE | Approved Apr 2019 | Approved 25 Jul 2019 | n/a | Submission December 2019 |
| Nordic | Already approved | Approved 14 Jan 2019 | n/a | Approved 14 Jan 2019 |
| Hansa | Already approved | Approved 28 Jan 2019 | n/a | Approved 20 Feb 2019 |
Table 2 – Capacity Calculation methodologies in 2019
Implementation monitoring
The CACM Cost Report 2017 and the CACM Cost Report 2018 submitted to NRAs respectively in April 2019 and in September 2019 in accordance with Art. 80(1) of the CACM Regulation includes the costs of coordinated activities of all NEMOs and/or all TSOs, and costs incurred for activities performed by NEMOs or by TSOs and NEMOs in a certain region, in relation to single day-ahead and intraday market coupling.
In August 2019, ENTSO-E issued the 5th edition of the annual report on the progress and potential problems with the implementation of FCA, single day-ahead coupling and single intraday coupling (a “Market Report”) in pursuance of Art. 82(2)(a) CACM and Art. 63(1)(a) FCA. Furthermore, a biennial “Report on Capacity Calculation and Allocation” was submitted to ACER in August 2019 in accordance with Art. 82(2)(b) and 31(2) of CACM and Art. 63(1)(c) and 26(1) of FCA.
Key dates & documents
12 Apr 2019
Submission to NRAs of the CACM Cost Report 2017
20 Sep 2019
Submission to NRAs of the CACM Cost Report 2018
14 Aug 2019
Submission to ACER of the ENTSO-E Market Report
14 Aug 2019
Submission to ACER of the ENTSO-E Report on Capacity Calculation and Allocation
The Forward Capacity Allocation Regulation
The FCA Regulation, which entered into force on 17 October 2016, sets out rules regarding the type of long-term transmission rights (LTTRs) that can be allocated via explicit auction, and the way holders of transmission rights are compensated in case their right is curtailed.
The overarching goal is to promote the development of liquid and competitive forward markets in a coordinated manner across Europe and provide market participants with the ability to hedge their risk associated with cross-border electricity trading.
Methodologies
Regarding the implementation tasks at the regional level, some CCRs delivered common capacity calculation methodologies for long-term time frames (Art. 10.1 FCA) and methodologies for splitting long-term cross-zonal capacity (Art. 16.1 FCA).
| LT timeframes (Art. 10.1) | Splitting LT cross-zonal capacity (Art. 16.1) | |
|---|---|---|
| Hansa | Submitted 18 Jun 2019 Public consultation 15 Apr – 15 May 2019 | Submitted 18 Jun 2019 Public consultation 27 Mar – 25 Apr 2019 |
| Core | Submitted 21 Aug 2019 Public consultation 10 Jun – 10 Jul 2019 |
|
| SWE6 | Public consultation 15 Mar – 15 Apr 2019 1st submission 15 May 20197 | Public consultation 1 – 30 Apr 20198 |
Table 3 – Capacity Calculation methodologies for FCA
6 Both methodologies have been approved in March 2020.
7 The 2nd submission took place in January 2020.
8 The methodology has been submitted in January 2020.
In accordance with Art. 31.1 of the FCA Regulation, ACER approved in October 2019 the second amendment to the Core TSOs’ regional design of LTTRs that implemented financial transmission rights options at specific bidding zone borders. The third amendment to the Core TSOs’ regional design of LTTRs, submitted in December 2019, introduces the switch from physical transmission rights with the use-it-or-sell-it principle to financial transmission rights on specific bidding zone borders. This third amendment does not change the impact of the previously approved amendment on the objectives of the FCA Regulation.
Key dates & documents
4 Apr 2019
Submission of the 2nd amendment to the Core TSOs’ regional design of LTTRs
12 Dec 2019
Submission of the 3rd amendment to the Core TSOs’ regional design of LTTRs
7 Feb – 7 Mar 2019
Public consultation on the 2nd amendment to the Core TSOs’ regional design of LTTRs
18 Dec 2019 – 26 Jan 2020
Public consultation on the 3rd amendment to the Core TSOs’ regional design of LTTRs
Following the all NRAs’ request for amendment to the joint proposal for a methodology for sharing congestion income from FCA (Art. 57.1 FCA), all TSOs submitted the amended version in March 2019 and all NRAs approved it in May 2019.
All TSOs have elaborated a reviewed Harmonised Allocation Rules (HAR) proposal which was submitted in July 2019 and approved by ACER in October 2019, in accordance with Art. 68.5 of the HAR.
Finally, ENTSO-E has coordinated the preparation of the All TSOs’ proposal for the methodology for sharing costs incurred to ensure firmness and remuneration of long- term transmission rights pursuant to Art. 61 (FCA).
The Electricity Balancing Regulation
Efficient balancing markets, in which all resources are empowered to participate on a level playing field, shall ensure security of supply at the lowest cost and can deliver environmental benefits by reducing the need for back-up generation. The Electricity Balancing Regulation (EB Reg.) sets a framework for common European rules and European platforms for cross-border balancing markets. The balancing processes are organised in the following steps:
- Frequency containment reserves (FCR)9, which stabilise the frequency after a disturbance at a steady-state value by a joint action of FCR within the whole synchronous area;
- Frequency restoration reserves with automatic activation (aFRR) and frequency restoration reserves with manual activation (mFRR): these are activated to control the frequency toward its set point value and replace FCR;
- Replacement reserves (RR), which replace and/or complement FRR by activation of RR;
- Imbalance netting (IN), which reduces the amount of simultaneous and counteracting aFRR activations via imbalance netting power interchange.
9 The Guideline includes FCR in the balancing energy process but does not provide for an associated common platform.
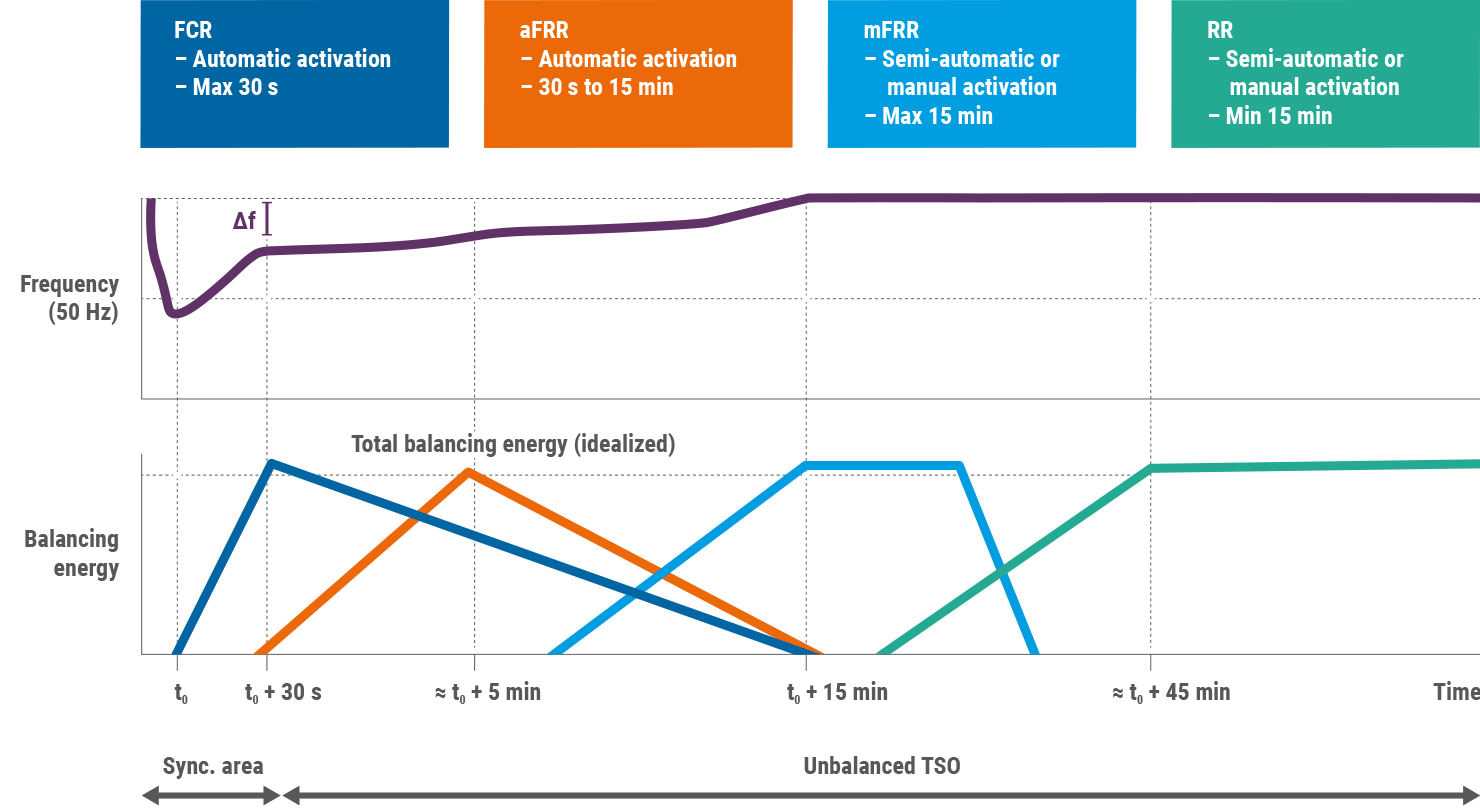
Figure 1 – Frequency restoration process
Ongoing or planned implementation activities include the development of several methodologies by all TSOs, with ENTSO-E acting as facilitator, as well as the implementation of the European balancing platforms.
The European balancing platforms
10 The platform was made operational in January 2020.
Further EB Reg. deliverables in 201911
| Further EB Reg. deliverables in 2019 | Key documents and dates | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Art. 25.2: | Proposal for a list of standard products for balancing capacity for frequency restoration reserves and replacement reserves | 15 May – 31 Jul 2019: | public consultation |
| 6 Jun 2019: | stakeholder workshop | ||
| 17 Dec 2019: | proposal submitted to all NRAs | ||
| Art. 29.3: | Proposal for a methodology for classifying the activation purposes of balancing energy bids | 11 Nov 2019: | 1st amendments submitted to all NRAs |
| Art. 30.1: | Proposal for pricing of balancing energy and cross-zonal capacity (CZC) used for the exchange of balancing energy (RR, FRR, IN) | 11 Feb 2019: | proposal submitted to all NRAs |
| Art. 40.1: | Proposal for a methodology for a co-optimised allocation process of CZC for the exchange of balancing capacity or sharing of reserves | 15 May – 30 Jul 2019: | public consultation |
| 6 Jun 2019: | stakeholder workshop | ||
| 17 Dec 2019: | proposal submitted to all NRAs | ||
| Art. 41.1: | Proposal for a methodology for a market-based allocation process of CZC for the exchange of balancing capacity or sharing of reserves (voluntary, each CCR to decide) | 20 Sep – 21 Oct 2019: | public consultations |
| 18 Dec 2019: | submission to relevant NRAs of Core and Hansa CCR TSOs’ proposals | ||
| Art. 42.1: | Core CCR TSOs’ proposal for a methodology for the allocation of cross-zonal capacity based on an economic efficiency analysis (voluntary, each CCR to decide) | 20 Sep – 21 Oct: | public consultation |
| 18 Dec 2019: | proposal submitted to relevant NRAs | ||
| Art. 50.1: | Proposal for TSO–TSO settlement of intended exchanges of energy as a result of the RR, mFRR, aFRR and/or RR processes | 11 Nov 2019: | 1st amendment to the proposal submitted to all NRAs |
| Art. 50.3.a: | Proposal for TSO–TSO settlement of intended exchanges of energy due to ramps and FCR within synchronous area continental Europe | 4 Jul 2019: | proposal submitted to relevant NRAs |
| Art. 50.3.b: | Proposal for TSO–TSO settlement of intended exchanges of energy due to ramps and FCR within synchronous area Nordics | 18 Dec 2019: | proposal submitted to relevant NRAs |
| Art. 50.4: | Proposal of TSO–TSO settlement of intended exchanges of energy due to ramp restrictions and FCR between synchronous areas | 18 Jun 2019: | proposal submitted to relevant NRAs |
| Art. 51.1.a: | Proposal for TSO-TSO settlement of unintended exchanges within synchronous area continental Europe | 4 Jul 2019: | proposal submitted to relevant NRAs |
| Art. 51.1.b: | Proposal for TSO–TSO settlement of unintended exchanges within synchronous area Nordics | 18 Jun 2019: | proposal submitted to relevant NRAs |
| Art. 51.2: | Proposal for TSO–TSO settlement of unintended exchanges between synchronous areas | 18 Jun 2019: | proposal submitted to relevant NRAs |
| Art. 52.2: | Proposal for imbalance settlement harmonisation | 11 Nov 2019: | 1st amendment to proposal submitted to all NRAs |
Table 4 – Further EB Reg. deliverables in 2019
11 Deliverables in accordance with Art. 25.2, 29.3, 30.1, 40.1, 50.1 and 52.2 will be subject to an ACER decision to be taken by mid-2020.
These developments are out of the scope of this Report and will be covered in the Annual Report 2020 to be drafted next year.
Transparency of capacity calculation by TSOs
The CEP, with the new Electricity Regulation, introduces a new regulatory framework for cross-border capacity calculation. Specifically, Article 16.8 demands that at least 70 % of the interconnection capacity shall be made available to the market (respecting operational security limits of internal and cross-zonal critical network elements and considering contingencies). The total amount of 30% can be used for the reliability margins, loop flows and internal flows on each critical network element.
In 2019, ENTSO-E and TSOs worked to develop a consistent approach across the regions towards Art. 16.8 with regard to its understanding, implementation and monitoring of compliance. ENTSO-E and TSOs also engaged in constructive discussions with ACER and NRAs on this topic.
Bidding zone review
In accordance with Art. 14.5 of the EU Electricity Regulation (2019/943), all TSOs submitted in October 2019 a proposal for the methodology and assumptions to be used in the bidding zone review process and for the alternative bidding zone configurations to be considered, with the annexed alternative bidding zone configurations drafted by the TSOs of each bidding zone review region.
All NRAs requested in December 2019 the re-submission of the proposal. Exchanges of view with stakeholders took place before and after submitting the above-mentioned proposal.
| All TSOs proposal | All NRAs request for re-submission | Stakeholder consultation |
|---|---|---|
| 4 Oct 2019: Submission to all NRAs of the proposal for the methodology and assumptions to be used in the bidding zone review process and for the alternative bidding zone configurations | 17 Dec 2019: All NRAs request for re-submission of the proposal for the methodology and assumptions to be used in the bidding zone review process and for the alternative bidding zone configurations12 | 8 Mar 2019: Symposium on model-based approach for alternative bidding zone configurations |
| 21 Oct 2019: Stakeholder webinar: Bidding Zone review methodology, assumptions and configurations | ||
Table 5 – Bidding Zone methodology and assumptions proposals
12 The proposal was re-submitted in February 2020.
Capacity Mechanisms
In 2019, ENTSO-E developed six methodologies, common rules and tools for the participation of foreign providers in capacity mechanisms.
As required by Art. 26.11 of the Electricity Regulation, ENTSO-E shall submit such methodologies to ACER by 5 July 2020.
Inter Transmission System Operator Compensation
The Inter Transmission System Operator Compensation (ITC) Agreement is a multiparty agreement concluded between ENTSO-E on the one hand, and ENTSO-E members and TSOs that comply with the Union law in the field of electricity or with the previous agreement on ITC, also referred to as “ITC Parties” in this context on the other,. It offers a single framework where European TSOs compensate each other for costs associated with hosting transit flows (i.e. facilitating the transfer of electricity between two countries). This mechanism aims to incentivise the hosting of cross border flows and thereby facilitates an effectively competitive pan-European electricity market.
The ITC mechanism is governed by Art. 49 of Reg. (EU) 943/2019. The ITC mechanism is further specified by Reg. (EU) 838/2010 on laying down guidelines relating to the inter-transmission system operator compensation mechanism and a common regulatory approach to transmission charging.
The ITC Agreement provides for an annual process in which the parties are required to provide and check the values for the calculation of the annual perimeter fee. Based on the preliminary data, the transit flows, also including the perimeter flows, are calculated (i.e. imports and exports of electricity to and from third countries).
According to Reg. (EU) 838/2010, ENTSO-E is mandated to determine the amount of losses incurred on national transmission systems by calculating the difference between: (1) the amount of losses actually incurred on the transmission system during the relevant period; and (2) the estimated amount of losses on the transmission system which would have been incurred on the system during the relevant period if no transit of electricity had occurred. In September 2019, ENTSO-E published the ITC Transit Losses Data Report 2018.
ACER publishes an annual monitoring report on ITC. To this end, ENTSO-E provides ACER with information on both quantitative data (preliminary and final data) and descriptive information (e.g. explanations for capacities not allocated according to Guidelines).
Download
ENTSO-E Annual Report 2019
This Annual Report covers the period from January to December 2019. It focuses on the legal mandates given to ENTSO-E. Activities covered in this report have been performed thanks to the 42 members of ENTSO-E who provide its financial resources and whose staff provides expertise to the Association.
Chapters:
- System Operation
- Market
- System Development
- Transparency Regulation
- Research, Development and Innovation
- Cybersecurity, Interoperability and Data
- TSO–DSO partnership and demand side flexibility





